Latest News
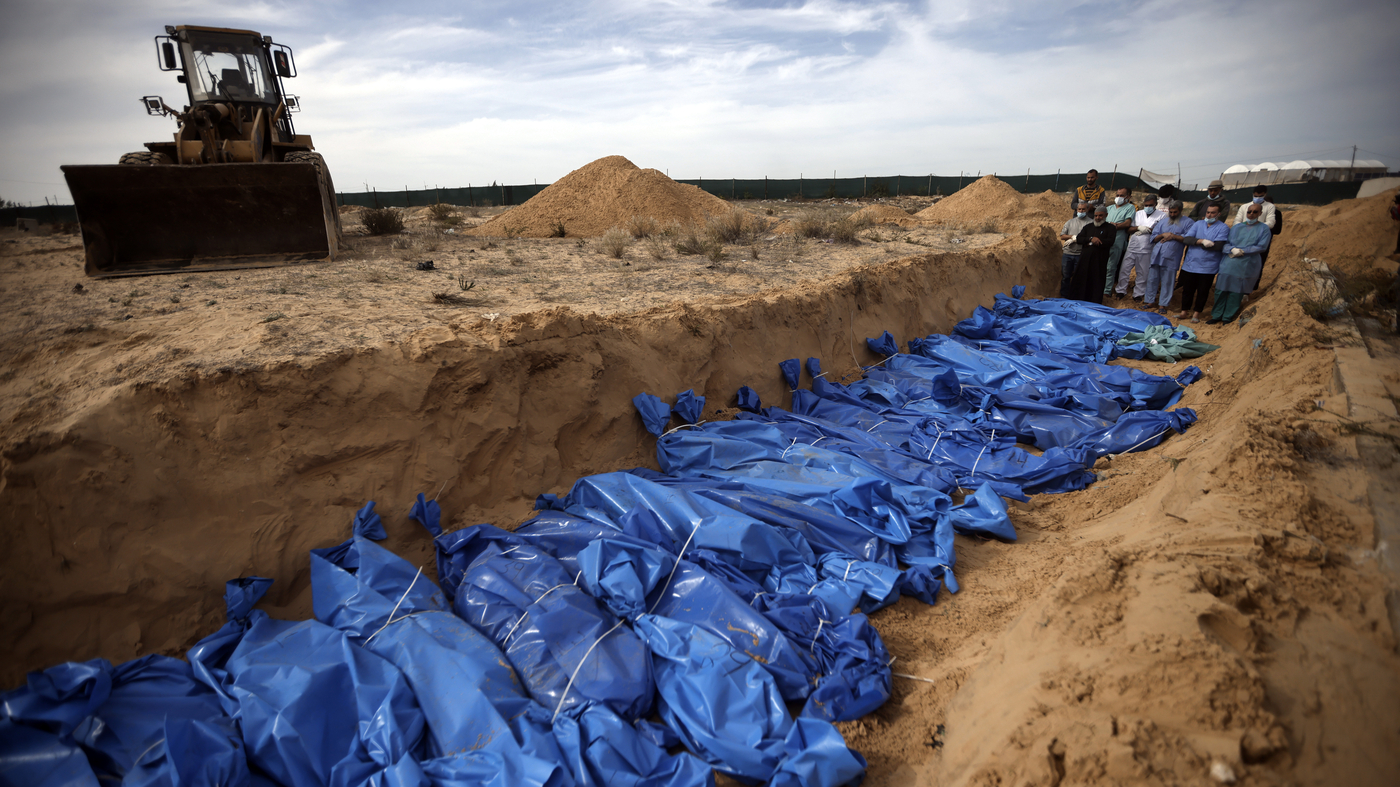
The upcoming months in Gaza are projected to becess deaths
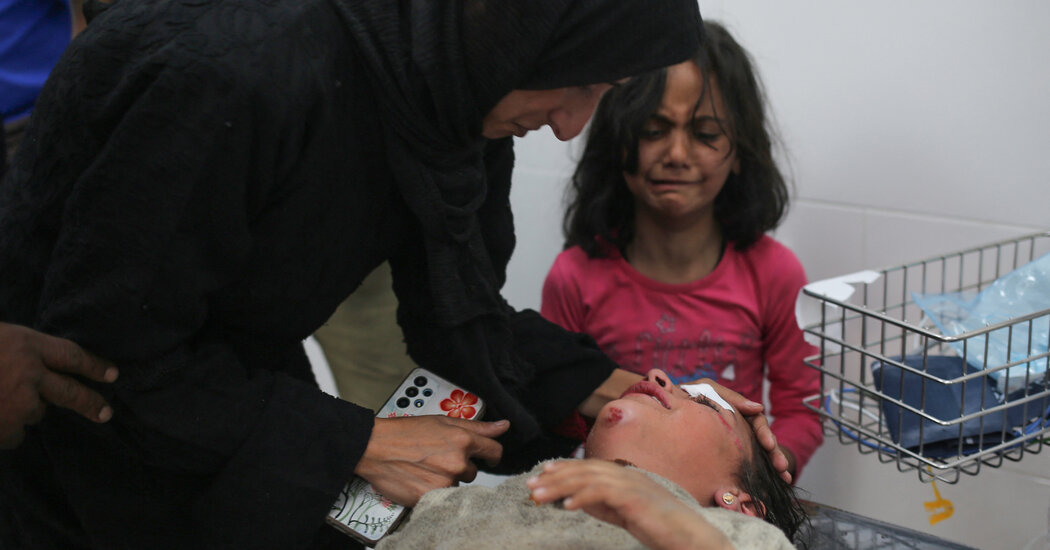
Israel has carried out its first airstrikes in Gaza since the beginning of the conflict between the militant group Hamas and the country’s military. The strikes, which have killed at least 11 people, targeted a maternity hospital in the city of Rafah, the Palestinian Health Ministry said. Over 38,000 people have been killed in the conflict, according to Gaza’s health ministry.
Read MoreThe fires in Texas offer a terrifying warning
Several wildfires in Texas, US have killed at least 15 people and destroyed thousands of homes. The Smokehouse Creek fire has also crossed into Oklahoma. Texas Governor Greg Abbott said that individual ranchers could suffer huge losses from the fires, but he was optimistic that the impact on the state’s cattle and beef industry would be minimal.
Read MoreThe major interstate in the Sierra Nevada was closed as a dangerous storm bore down
The National Weather Service has issued a blizzard warning for the Sierra Nevada in Northern California. The storm system is expected to bring 10 feet of snow to parts of the Sierra Nevada and winds will reach up to 150 mph. Further, a winter storm warning has also been issued for most of Northern California on Friday and Saturday.
Read MoreThe reason healthcare providers are not getting paid is due to Blackcat
A cyberattack on US-based healthcare services firm Change Healthcare has affected patients’ personal data like social security numbers, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) said on Tuesday. The hackers are believed to be Blackcat, which carried out the MGM casino breach last year. Change Healthcare is a middleman between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
Read MoreThe Legislature moved to protect the services after the court ruling
The US state of Alabama is considering legislation to protect clinics and doctors from prosecution and civil lawsuits over the death of embryos or the damage to them. This comes after Alabama’s highest court ruled that frozen embryos should be considered “children”. The bill will protect providers from prosecution and civil lawsuits over the death of an embryo or the damage to it.
Read MoreDeath tolls in Gaza have passed 30,000
Gaza’s health ministry has released a database of victims’ names after US President Biden said that he had “no confidence” in the figures they reported. Gaza’s health ministry published a database of victims’ names after Biden said he had “no confidence” in the figures they reported. In an interview with NPR, Biden said there is an estimated 10,000 people who are missing and presumed dead.
Read MoreSupreme Court seems to be torn over the ban
At the US Supreme Court, Justice Neil Gorsuch questioned the idea that the ATF could just change their interpretation of the machine gun law in order to ban bump stocks. In 2018, the federal government banned bump stocks for that reason, but gun enthusiasts have challenged the regulation in court, contending that only Congress has the power to enact such a ban.
Read MoreAlabama patients are running short of time
US’ Alabama Supreme Court has said that frozen embryos can be considered a child if they’re thawed after birth. The court ruled that freezing embryos can help people who want to have children but can’t get pregnant due to medical reasons. The court said that it’s up to the individual to decide whether to cryogenically freeze their embryos.
Read MoreIdaho prepares to execute a death row prisoner
In the US, 73-year-old death row inmate John Creech has been given a sedative before his scheduled execution on Wednesday. Creech was sentenced to death by lethal injection for the murder of a 22-year-old man in 1994. Creech’s spiritual adviser will be allowed to stand next to him with a hand on his shoulder during the execution.
Read MoreIn Arizona, abortion politics are playing out on the Senate campaign trail
Arizona Republicankari Lake said she thinks Alabama lawmakers “covering their butts” by considering a bill to protect in vitro fertilization (IVF) after the Alabama court ruled that frozen embryos are children. The National Republican Senatorial Committee issued a memo warning candidates to “clearly and reject” efforts to enshrine in vitro fertilization, a treatment that some clinics have paused in the wake of the ruling.
Read More