Latest News
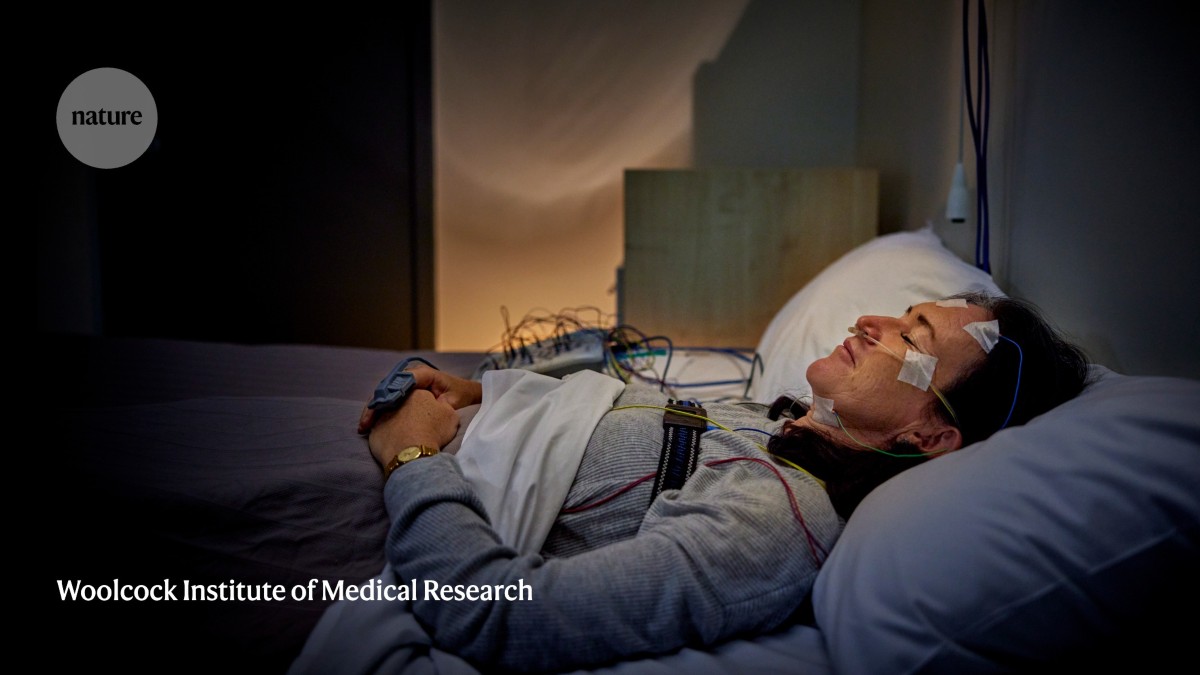
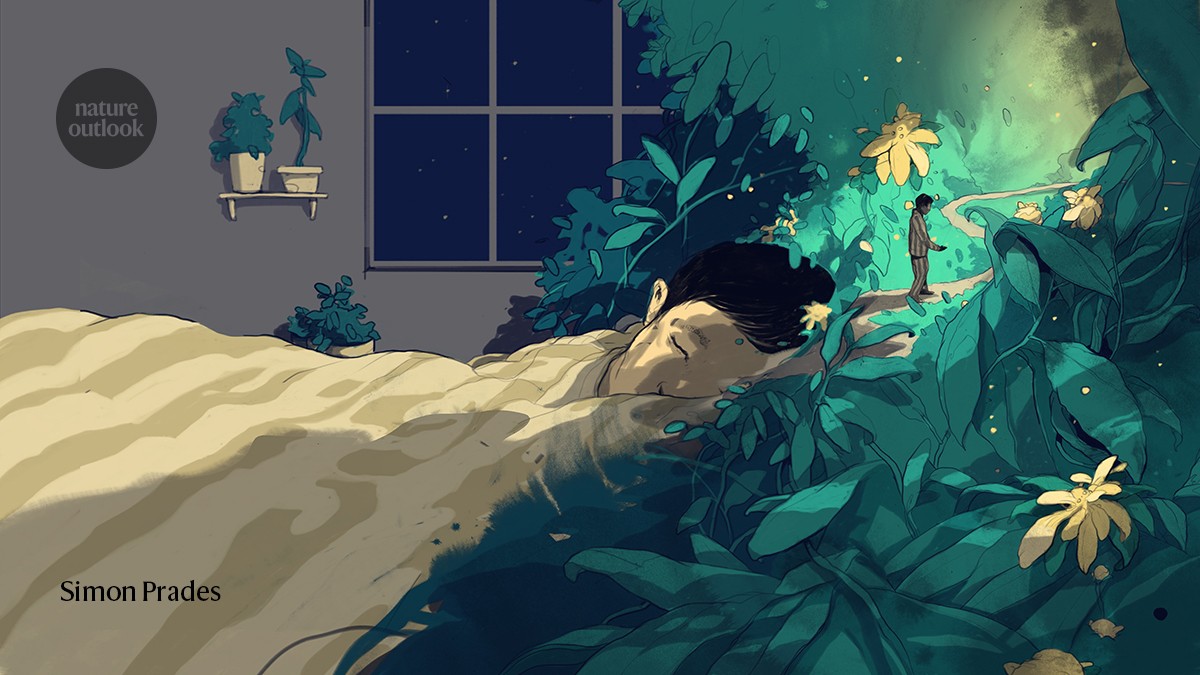
The road to a good night’s sleep is expensive and frustrating
In clinical trials, Idorsia showed that compared with people given a placebo, people who received daridorexant experienced significant improvements in daytime insomnia symptoms the following day. The main drawback to DOR drugs is not medical but financial: Their high cost keeps them out of reach for many people who could benefit from them, Buysse said.
Read MoreResearchers are trying to figure out why sleep is important
A study on fruit flies found that when they were deprived of sleep, they started dying as soon as they reached the end of their life span. Researchers also found that a sleep-deprived fruit fly had less amyloid andtau in its brain, a protein that is known to cause Alzheimer’s Disease. The flies that slept were placed in vibrating tubes.
Read MoreThe debate about brain clearance and dementia
Maiken Nedergaard, a neuroscientist at the University of Rochester in US, has claimed that people who report six hours or less of sleep a night are more likely to develop dementia later. In her latest paper, Nedergaard said that “we have mice that sleep completely normally”. She added that the fibers mounted in a hook can’t be carried on a mouse’s head.
Read MoreWhat will the cuts at the Centers for Disease Control do to global programs?
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) will have to reduce spending on contracts by at least a third, Robert Steinbrook, health research group director at the Public Citizen, said. This comes after President Donald Trump ordered a 25% reduction in staff and 35% reduction in contracts for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
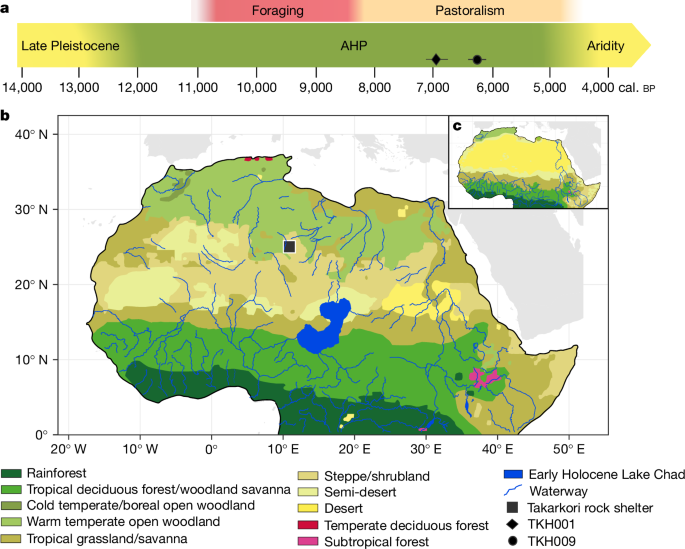
Read MoreThe first DNA profiles from ancient people who lived in a lush area of Africa
Researchers claim to have extracted ancient DNA from two women who died around 7,000 years ago in Libya to reconstruct the beginnings of the Saharans. The DNA profiles represent the first full Saharan genomes from the African Humid Period. Researchers said the DNA profiles represent the first full Saharan genomes from the African Humid Period and reveal that the people were remarkably isolated from other African populations.
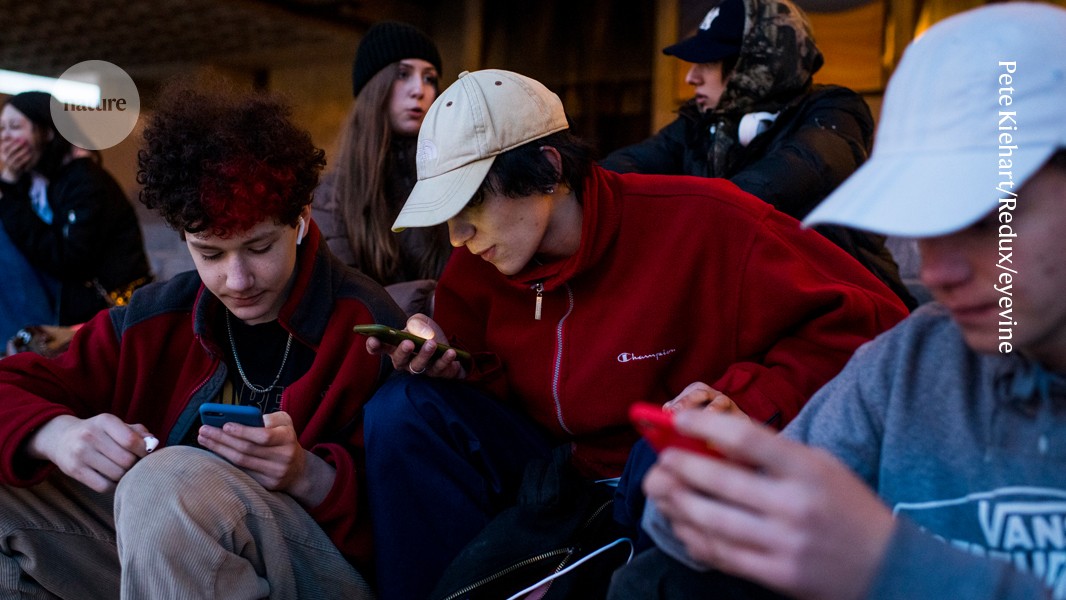
Read MoreTeens’mental health may be hurt by phones and social media
Social media may have an impact on mental health but it depends on an individual’s background, social media platforms they use and their view of the Internet, a study said. The study also found that young people’s response to social media fluctuates from one person to the next. However, it added that it is not known whether social media causes depression.
Read MoreThere are fears of big cuts to US AIDS prevention
US President Donald Trump’s administration has fired around 50 people from the infectious-disease office at the Department of Health and Human Services which worked to end the country’s HIV epidemic. The office had coordinated the implementation of the policy ending the HIV Epidemic in the US. It employed around 50 people, according to media reports.
Read MoreThere are fears of big cuts to US AIDS prevention
US President Donald Trump’s administration has fired around 50 people from the infectious-disease office at the Department of Health and Human Services which worked to end the country’s HIV epidemic. The office had coordinated the implementation of the policy ending the HIV Epidemic in the US. It employed around 50 people, according to media reports.
Read MoreMany in leadership at federal health agencies have been fired
The US Department of Health and Human Services is planning to move some people around, an e-mail obtained by Nature showed. Several NIH leaders were offered the chance to transfer to the Indian Health Service, the division of HHS that provides medical care to Indigenous people in the US, the email stated. Earlier, the Trump administration announced plans to dismiss 10,000 people.
Read MoreThe Trump team withdrew millions of dollars for addiction and mental health care
US President Donald Trump’s administration has cut 20,000 jobs in the Health and Human Services (HHS) department, as it restructures the department. The department includes the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, the Food and Drug Administration, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and other smaller divisions.
Read More