The cells that make up turbinate-homing IgA-secreting are located in the nasal lymphoid tissues
by admin
T-cells: a computational tool to analyze and predict the fate of lung-resident memory B cells with Platypus (Extended Abstract)
Tan, H-X. Lung-resident memory B cells established after pulmonary influenza infection display distinct transcriptional and phenotypic profiles. Sci. Immunol. 7, eabf5314 (2022).
Nolan, S. and others. The T-cellreceptorb sequence and binding associations are available in a large-scale database. Preprints can be found at Research Square.
Human T cellsresident memory are found in health and disease. Mucosal Immunol. 15, numbered 389, made its appearance in2022.
Yermanos, A. et al. Platypus is an open-access software used to integrate immune repertoires with transcriptomes. There is a Genom. Bioinform. 3, lqab023 will be in the year 2021.
Kusnadi, A. et al. Severely ill COVID-19 patients have exhaustion features in T cells. Sci. Immunol. 6, eabe4782 (2021).
B Cells in Normal Human Lymph Node T-Follicular Helper and germinal center B cells accessed via fine needle aspirations
Havenar-Daughton, C. et al. Normal human lymph node T follicular helper cells and germinal center B cells accessed via fine needle aspirations. J. Immunol. The methods are 479 and 112746.
The model of the HIV neutralizing Antibody generation problem is studied by Havenar-Daughton. Immunol. Rev. 275, 49–61 (2017).
Hoehn, K. B. et al. Repertoire-wide phylogenetic models of B cell molecular evolution reveal evolutionary signatures of aging and vaccination. It was Proc. The National Acad. is the Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 22664–22672 (2019).
Zumaquero, E. et al. IFNγ induces epigenetic programming of human T-bethi B cells and promotes TLR7/8 and IL-21 induced differentiation. e Life 8, e41641.
Single cell analysis of Streptococcus tonsillitis: Rep. 112682 is in 23. J. M. et al
M. Duan was one of the authors of the article. Understanding heterogeneity of human bone marrow blood cells can be accomplished by single cell analyses. The cell Rep. 112682 is in 23.
J. M. et al. The group is reacquainted. Streptococcus tonsillitis is a disease that has a deficiency of T FH cells. Sci. Transl. The Med. 11 was published on the same day.
Source: Immunological memory diversity in the human upper airway
IgBLAST: An immunoglobulin variable sequence analysis tool for identification of HIV envelope trimers in human and mouse plasmas. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D256-D261 2005
Holla, P. et al. Shared transcriptional profiles of atypical B cells suggest common drivers of expansion and function in malaria, HIV, and autoimmunity. Sci. Adv.7, eabg8384 will take place in the year 2021.
Human and mouse immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes are included in the database. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D256–D261 (2005).
Nouri, N. & Kleinstein, S. H. Somatic hypermutation analysis for improved identification of B cell clonal families from next-generation sequencing data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 16, e1007977 (2020).
Ye, J., Ma, N., Madden, T. L. & Ostell, J. M. IgBLAST: an immunoglobulin variable domain sequence analysis tool. The names of the acids in the compendium are Nucleic Acids Res. 41 and W34.
Lundgren, A. et al. Plasmablasts in previously immunologically naïve COVID-19 patients express markers indicating mucosal homing and secrete antibodies cross-reacting with SARS-CoV-2 variants and other beta-coronaviruses. It’s Clin. Exp. Immunol. 213, 173–189 (2023).
Hastie, K. M. Potent Omicron-neutralizing antibodies isolated from a patient vaccinated 6 months before Omicron emergence. Cell Rep. 42, 112421 (2023).
Lee, J. H. A broadly neutralizing antibody targets the dynamic HIV envelope trimer apex via a long, rigidified, and anionic β-hairpin structure. There are Immunity 46, 690–702.
The missing piece of the airway defence is olfactory immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. It can be found in https://doi.org/10.1137/s41577-023-00972-9.
The role of the Gut IgA class switch on the colonization and infiltration of germinal peyer patches of the subepithelial dome
A group of people, A. Biram, A. BCR affinity differentially regulates colonization of the subepithelial dome and infiltration into germinal centers within Peyer’s patches. Nat. Immunol. 20, 482–492 (2019).
The Gut IgA class switch isn’t related to the germ when there is no CD40 in the tissue. J. Immunol. 177, 7772–7783 (2006).
Hartwell, B. L. et al. Administering a vaccine with immunogens that are lipid-conjugated reduces the risk of an immune response. Sci. Transl. There were 14 Meds during the year.
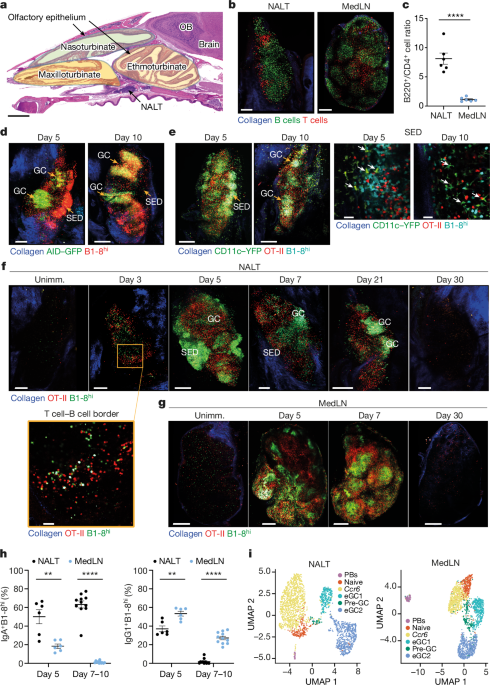
Source: Turbinate-homing IgA-secreting cells originate in the nasal lymphoid tissues
A remark on the role of B cell affinity in immune response of the nasal lymphoid tissue of the nose (NALTs-associated with the nose)
Ualiyeva et al. A nasal cell shows the heterogeneity of tuft cells, which play a role in olfactory stem cell proliferation. There is a science of Immunol. It was 9, the year of 204.
The article was titled “A. Pizzolla, et al.” The recall is supported by a certain number of Nasal Lymphoid tissues (NALTs) that are associated with the nose. Proc. There is a Natl Acad. The journal USA 114, 5225–5230.
Role of BCR affinity in T cell- dependent antibody responses. Nat. Immunol. 3 was written in 2002
Biram, A. et al. The affected germinal center reactions are monocyte recruitment and impaired metabolism. The Immunity 55, 454, and 450 are in use today.
Schwickert, T. A. A checkpoint regulates B cell entry into the germinal center. J. Exp. The medicy was in 112, 122, and 125 in 2011.
Bemark, M., Pitcher, M. J., Dionisi, C. & Spencer, J. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue: a microbiota-driven hub of B cell immunity. Trends Immunol. 45, 211–223 (2024).
T. Okada, et al. Antigen B cells form motile conjugates with other T cells when they are in the T zone. PLoS Biol. 3, e150 (2005).
Source: Turbinate-homing IgA-secreting cells originate in the nasal lymphoid tissues
YTHDF2 suppresses the plasmablast genetic program and promotes germinal center formation. Cell Rep. 30, 1910-1922 (2020)
Grenov, A., Hezroni, H., Lasman, L., Hanna, J. H. & Shulman, Z. YTHDF2 suppresses the plasmablast genetic program and promotes germinal center formation. The Cell Rep. 39 will be available in the year 2020.
Biram, A. et al. B cell diversification is uncoupled from SAP-mediated selection forces in chronic germinal centers within Peyer’s patches. Cell Rep. 30, 1910–1922 (2020).
Tsuji, M. et al. Requirement for lymphoid tissue-inducer cells in isolated follicle formation and T cell-independent immunoglobulin A generation is in the gut. Immunity 29, 261–271 (2008).
T cells with IgA class switch recombination occurring before germinal center formation are restricted to the GALT. J. Immunol. 184, 3545–3553 (2010).
Underhill, G. H., Minges Wols, H. A., Fornek, J. L., Witte, P. L. & Kansas, G. S. IgG plasma cells display a unique spectrum of leukocyte adhesion and homing molecules. Blood 99 was published in 2002.
Hieshima, K. et al. CC chemokine 25 and 28 are used for extravasation of Ig A cells. J. Immunol. 3668–3675 was published in 2004.
Linehan, J. L. et al. Generation of Th17 cells in response to intranasal infection requires TGF-β1 from dendritic cells and IL-6 from CD301b+ dendritic cells. Proc. A journal of the Natl Acad. The USSci. USA 112 was published in 2015.
There is a protective effect of cross-presenting microglia against a virus that causes a rash on the brain. There is a scientific discipline called Immunol. 5, eabb1817 in 2020.
Source: Turbinate-homing IgA-secreting cells originate in the nasal lymphoid tissues
Mapping Systemic Inflammation and Antibody Responses in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Case Study of J.-O. et al
Harkema, J. R., Carey, S. A., Wagner, J. G., Dintzis, S. M. & Liggitt, D. in Comparative Anatomy and Histology (eds Treuting, P. M. & Dintzis, S. M.) 71–94, Ch. 6 (Academic, 2012).
Gruber, C. N. et al. Mapping systemic inflammation and antibody responses in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Cell 183 was used in 2020.
Jin, J.-O. et al. Inflammation agent evaluation includes lymphoid tissue and injection route- dependent dendritic cell activation. J. Vis. The paper was published on October 2nd, 2018: Exp.
Source: Turbinate-homing IgA-secreting cells originate in the nasal lymphoid tissues
High-dimensional cell-level analysis of tissues: A single cell ribonucleic acid sequence as a single-cell recombinant spectrometer
Li, W., Germain, R.N., and Gerner, M Y., studied high-dimensional cell-level analysis of tissues. Nat. Protoc. 14, 1708–1733, was published in 2019.
Victora, G. D. et al. Germinal center dynamics revealed by multiphoton microscopy with a photoactivatable fluorescent reporter. Cell 143, 592–605 (2010).
Keren-Shaul, H. et al. A single-cell ribonucleic acid sequence is combined with an experimental and analytical methodology for index sorting. There is Nat. Protoc. 14, 1841–1862 (2019).
Subramanian, A. et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. It was Proc. There is a Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550 (2005).
A study has found that mucus-resident IgA-secreting cells originate in nasal lymphoid tissues. Researchers said this helps to distinguish the germinal centres within Peyer’s patches from the nasal lymphoid tissue. T cells with IgA class switch recombination occurring before germinal centre formation are restricted to the nasal lymphoid tissues, the study said.